C# Queue源码剖析
Queue表示对象的先进先出集合。实现了ICollection接口,可以由数组或链表两种形式实现,在.NET中是以数组的形式实现的。
概念
队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表头(head)进行删除操作,而在表尾(tail)进行插入操作。
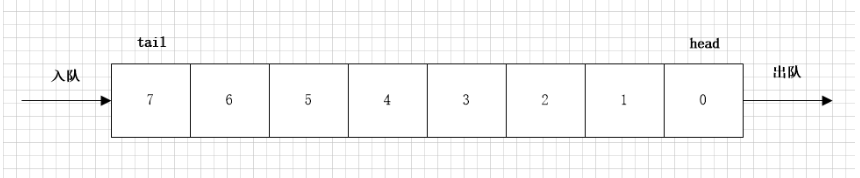
队列的数据元素又称为队列元素。在队列中插入一个队列元素称为入队,从队列中删除一个队列元素成为出队。因为队列只允许在一端插入,在另一端删除,所以只有最早进入队列的元素才能最先从队列中删除,故队列又称为先进先出(FIFO—first in first out)线性表
队列可以分为顺序队列和循环队列,.NET中为了提高空间的利用率,采用的是循环队列。
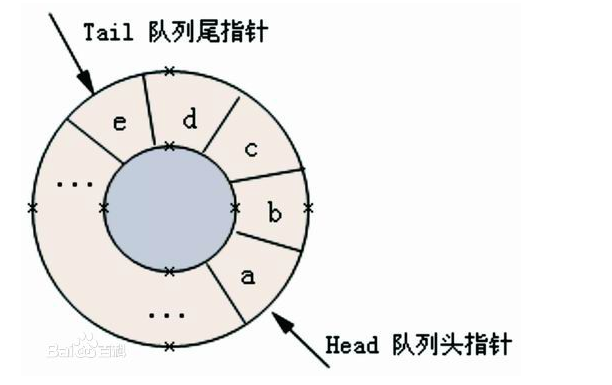
循环队列
为充分利用向量空间,克服 ”假溢出”(由于入队和出队操作中,头尾指针只增加不减小,致使被删元素的空间永远无法重新利用) 现象的方法是:将向量空间想象为一个首尾相接的圆环,并称这种向量为循环向量。存储在其中的队列称为循环队列(Circular Queue)。
判断是空还是满
循环队列中,由于入队时尾指针向前追赶头指针;出队时头指针向前追赶尾指针,造成空队列和满队列时头尾指针均相等。因此,无法通过条件front==rear来判别队列是”空”还是”满”. .NET使用以下方法判断空队列和满队列(实际.NET中,队列的长度时自动扩容的):
- 私有成员
_size = 0时,为空队列。 _size == _array.Length时(_array为Queue内部维护的实际数据数组),为满队列,这个时候会进行自动扩容(新建一个2倍于原容量的数组)。
Queue 基本成员
private T[] _array;
private int _head; // 表头
private int _tail; // 表尾
private int _size; // 队列元素数量
private int _version;
[NonSerialized]
private Object _syncRoot;
private const int _MinimumGrow = 4; // 最小增长值
private const int _ShrinkThreshold = 32; // 收缩阈值
private const int _GrowFactor = 200; // 每次增长双倍
private const int _DefaultCapacity = 4; // 默认容量
static T[] _emptyArray = new T[0]; //空数组
Queue 初始化函数
public Queue() {
_array = _emptyArray;
}
public Queue(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0)
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.capacity, ExceptionResource.ArgumentOutOfRange_NeedNonNegNumRequired);
_array = new T[capacity];
_head = 0;
_tail = 0;
_size = 0;
}
public Queue(IEnumerable<T> collection){
if (collection == null)
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.collection);
_array = new T[_DefaultCapacity];
_size = 0;
_version = 0;
using(IEnumerator<T> en = collection.GetEnumerator()) {
while(en.MoveNext()) {
Enqueue(en.Current);
}
}
}
Queue 入队
入队的方法:Enqueue(T item)
public void Enqueue(T item)
{
//动态扩容
if (_size == _array.Length)
{
// 扩大2倍
int newcapacity = (int)((long)_array.Length * (long)_GrowFactor / 100);
if (newcapacity < _array.Length + _MinimumGrow)
{
newcapacity = _array.Length + _MinimumGrow;
}
// 设置容量
SetCapacity(newcapacity);
}
// 设置队尾元素
_array[_tail] = item;
// 下一个队尾的索引计算
// 此公式与抑制了队尾索引不会超过数据数组长度
// 从而避免了数据溢出的产生(同时也会导致队尾索引会小于队头索引,需要分情况进行处理)。
_tail = (_tail + 1) % _array.Length;
_size++;
_version++;
}
Queue 出队
出队有两种方法
public T Peek():返回位于 Queue 开始处的对象但不将其移除。public T Dequeue():移除并返回位于 Queue 开始处的对象。
// Peek()简单粗暴,通过_array[_head]索引直接返回数据。
public T Peek()
{
if (_size == 0)
ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException(ExceptionResource.InvalidOperation_EmptyQueue);
return _array[_head];
}
// Queue没有提供Remove方法,但是Dequeue具有删除功能并返回头元素。
// 被移除的元素直接指向null(空引用)。并且头元素索引向前移动
public T Dequeue()
{
if (_size == 0)
ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException(ExceptionResource.InvalidOperation_EmptyQueue);
T removed = _array[_head];
// 被移除的元素直接指向null(空引用)
_array[_head] = default(T);
// 头指针也向后移动一位
_head = (_head + 1) % _array.Length;
_size--;
_version++;
return removed;
}
Queue 查询
Contains(T item)判断队列中是否至少包含一个匹配的元素存在 是则返回true,否则返回false。
public bool Contains(T item)
{
int index = _head;
int count = _size;
EqualityComparer<T> c = EqualityComparer<T>.Default;
// while遍历数组中的元素
while (count-- > 0)
{
if (((Object) item) == null)
{
if (((Object) _array[index]) == null)
return true;
}
// 用比较器比较是否相等
else if (_array[index] != null && c.Equals(_array[index], item))
{
return true;
}
// 用临时指针index代替head进行移动遍历
index = (index + 1) % _array.Length;
}
return false;
}
Queue 容量调整
容量调整,可以重置队列空间,如果元素数小于当前容量的 90%,将容量设置为 Queue中的实际元素数。
// 整理队列空间
public void TrimExcess()
{
int threshold = (int)(((double)_array.Length) * 0.9);
if( _size < threshold ) {
SetCapacity(_size);
}
}
private void SetCapacity(int capacity)
{
//创建新数组
T[] newarray = new T[capacity];
if (_size > 0)
{
if (_head < _tail)
{
//头索引小于尾索引
Array.Copy(_array, _head, newarray, 0, _size);
}
else
{
//头索引大于尾索引
Array.Copy(_array, _head, newarray, 0, _array.Length - _head);
Array.Copy(_array, 0, newarray, _array.Length - _head, _tail);
}
}
_array = newarray;
_head = 0;
_tail = (_size == capacity) ? 0 : _size;
_version++;
}
最后
- Queue可以通过
TrimExcess()方法,将容量下降到实际元素的数量. - Queue允许重复的元素。
- Queue和Stack主要是用来存储临时信息的。
